Zhiyang Chen
![]() Postdoc, Westlake University (2024)
Postdoc, Westlake University (2024)
I am currently a member of Machine Perception & Learning (MAPLE) Lab, Westlake University, working with Prof. Guo-Jun Qi. I obtained my Ph.D. from Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences in June 2024.
My research interests includes multi-modal content perception and generation, and I currently focus on building large multimodal models.
If you are looking for Ph.D. or research intern opportunities in these areas, feel free to contact me via email.

Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "News
Selected Publications (view all )

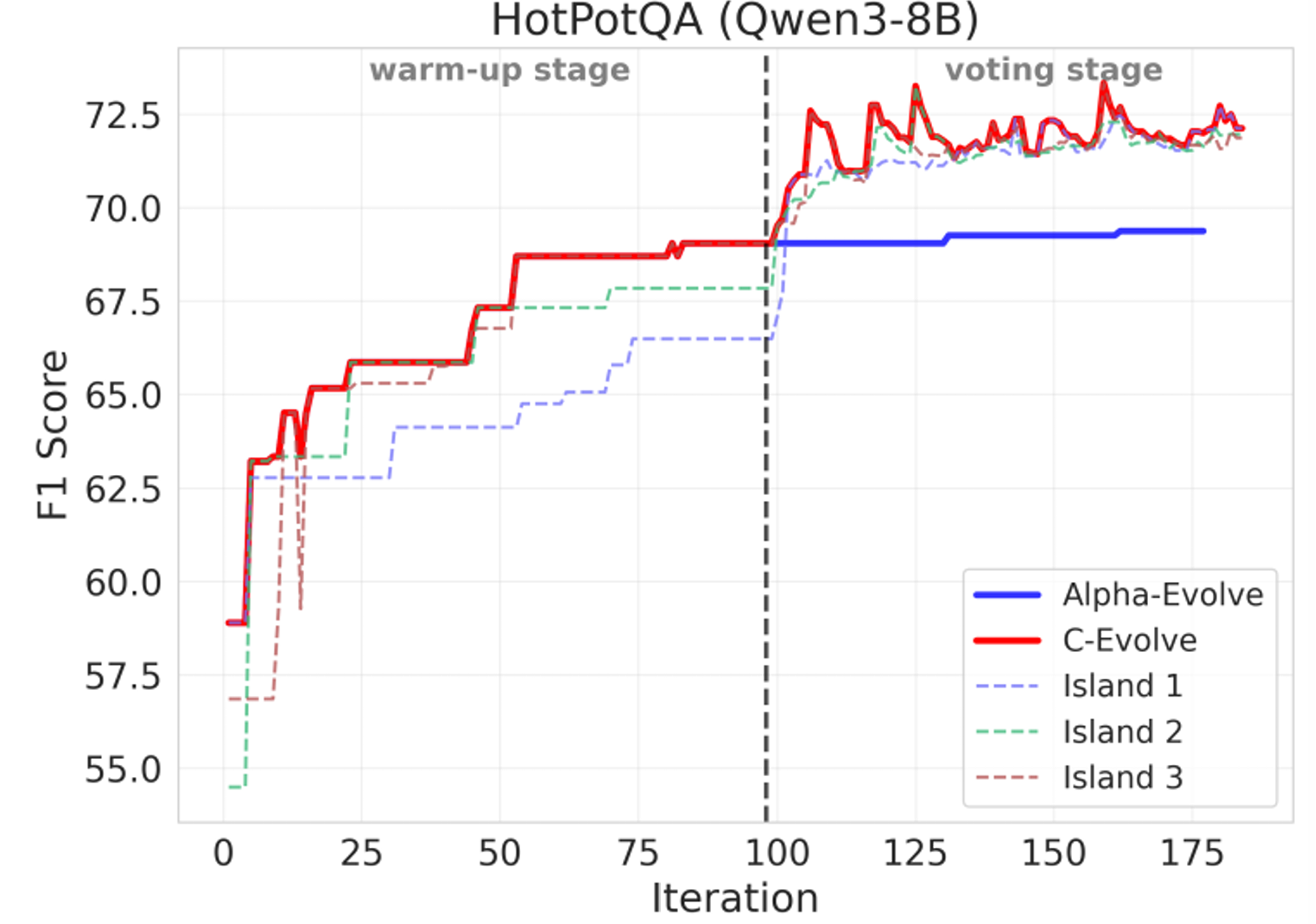
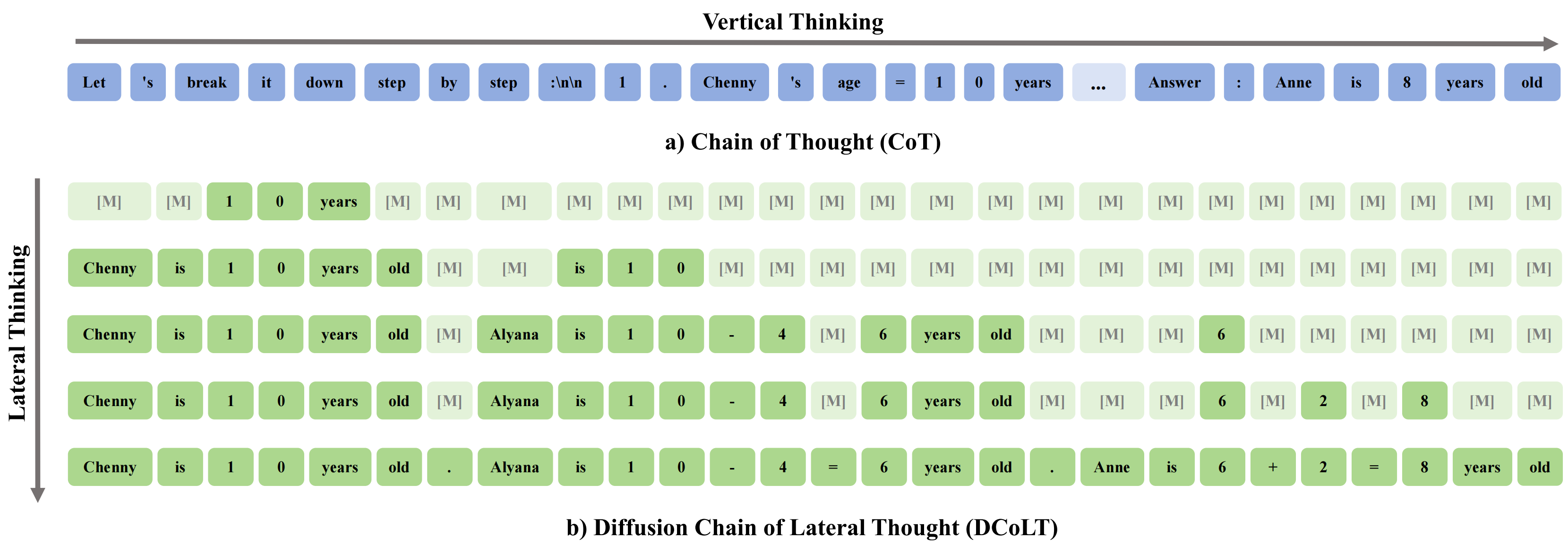
Don't Settle Too Early: Self-Reflective Remasking for Diffusion Language Models
Zemin Huang, Yuhang Wang, Zhiyang Chen#, Guo-Jun Qi# (# corresponding author)
arxiv 2025
We propose RemeDi, a new diffusion language model that introduces remasking allowing model to detect and resample low-confidence tokens during generation.

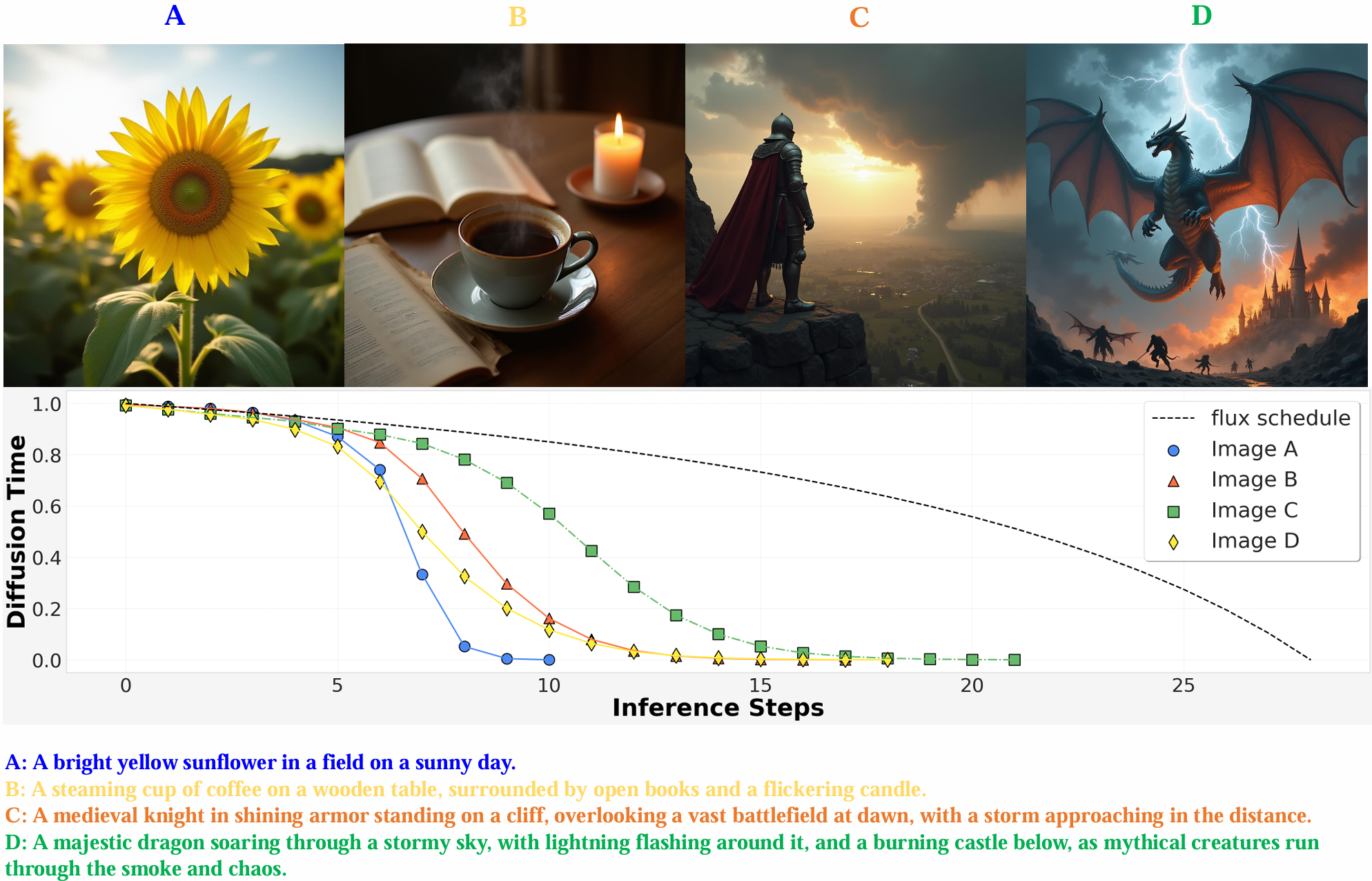
Schedule On the Fly: Diffusion Time Prediction for Faster and Better Image Generation
Zilyu Ye, Zhiyang Chen#, Tiancheng Li, Zemin Huang, Weijian Luo, Guo-Jun Qi# (# corresponding author)
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2025
A Reforcement-Tuned Diffusion Model that can adjust the noise schedule on the fly, assigning fewer denoising steps on simple samples while more steps on complex ones.

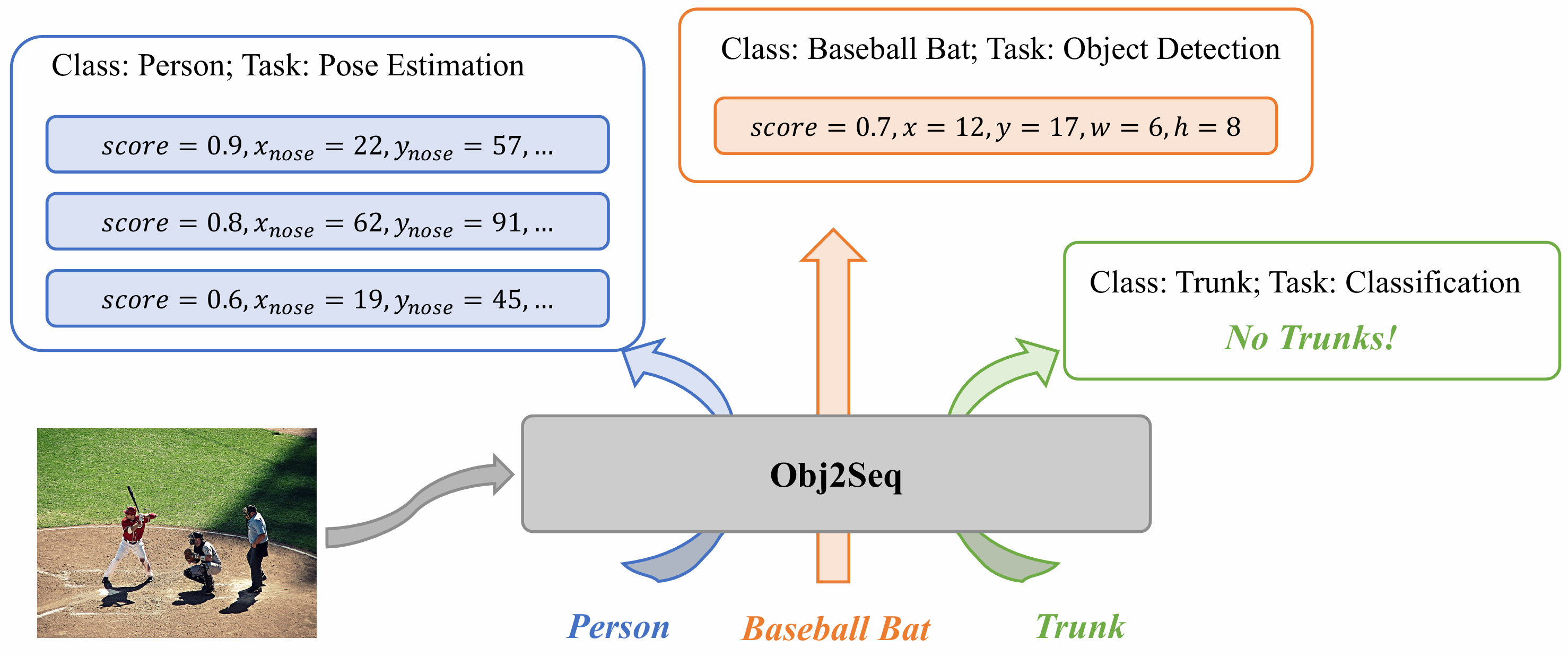
Obj2Seq: Formatting objects as sequences with class prompts for visual tasks
Zhiyang Chen, Yousong Zhu, Zhaowen Li, Fan Yang, Wei Li, Hanxin Wang, Chaoyang Zhao, Liwei Wu, Rui Zhao, Jinqiao Wang, Ming Tang
Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2022 Spotlight
We propose a general definition that encompasses a wide range of visual tasks, so that all their outputs can be decoded in an identical way: treating objects as fundamental units and generating multiple sequences based on the input image and class prompts. According to this, we build a language-guided general vision model that can meet diverse task requirements and achieve comparable performance with specialized models.

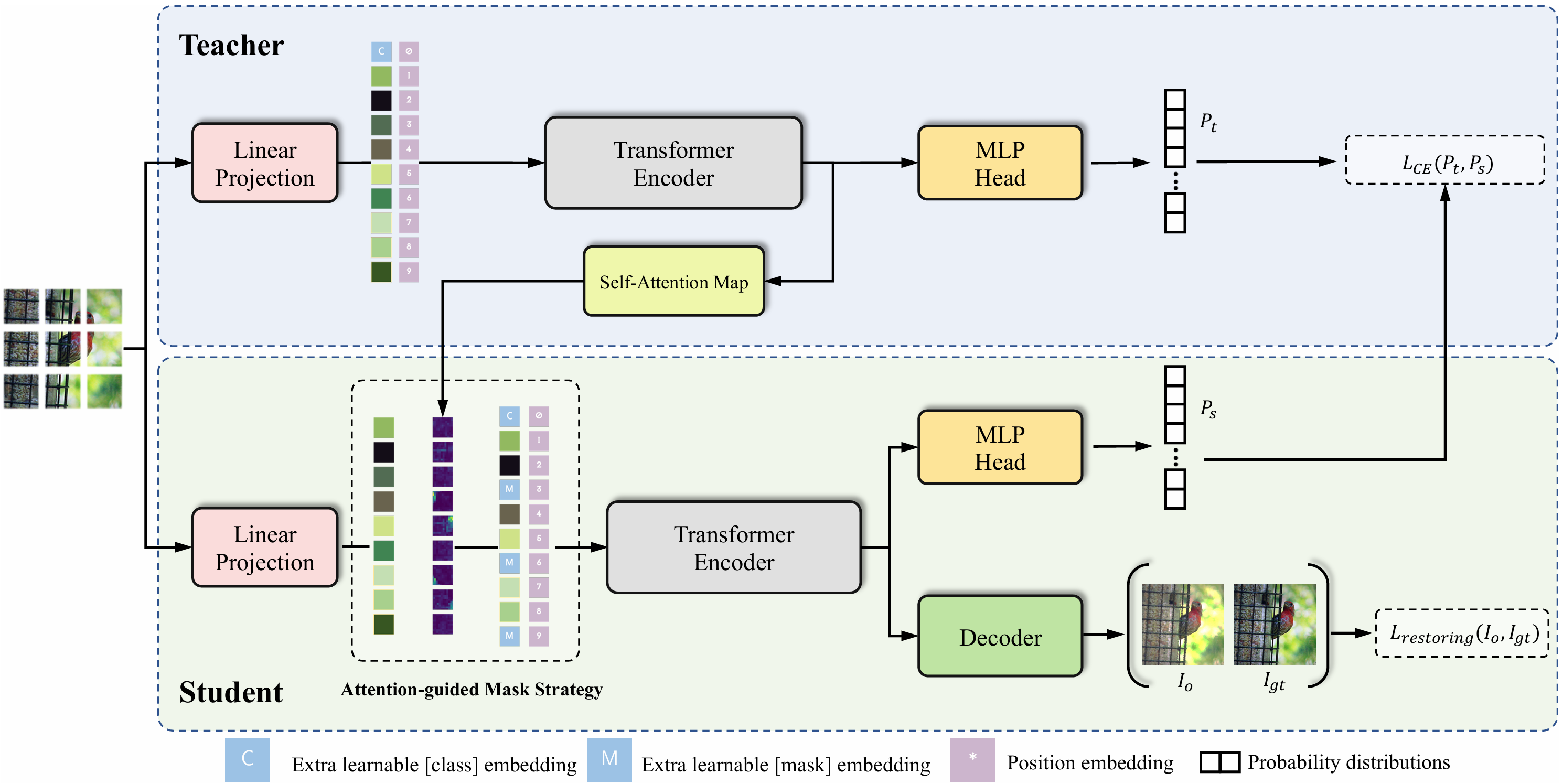
MST: Masked Self-Supervised Transformer for Visual Representation
Zhaowen Li, Zhiyang Chen, Fan Yang, Wei Li, Yousong Zhu, Chaoyang Zhao, Rui Deng, Liwei Wu, Rui Zhao, Ming Tang, Jinqiao Wang
Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2021
This paper is an early work to introduce Masked Image Modeling in self-supervised learning. MST utilizes self-attention map to mask background image tokens, and supervises with a pixel-level restoration loss to preserve fine-grained information, in addition to common contrastive learning. MST helps a lot in downstream tasks.

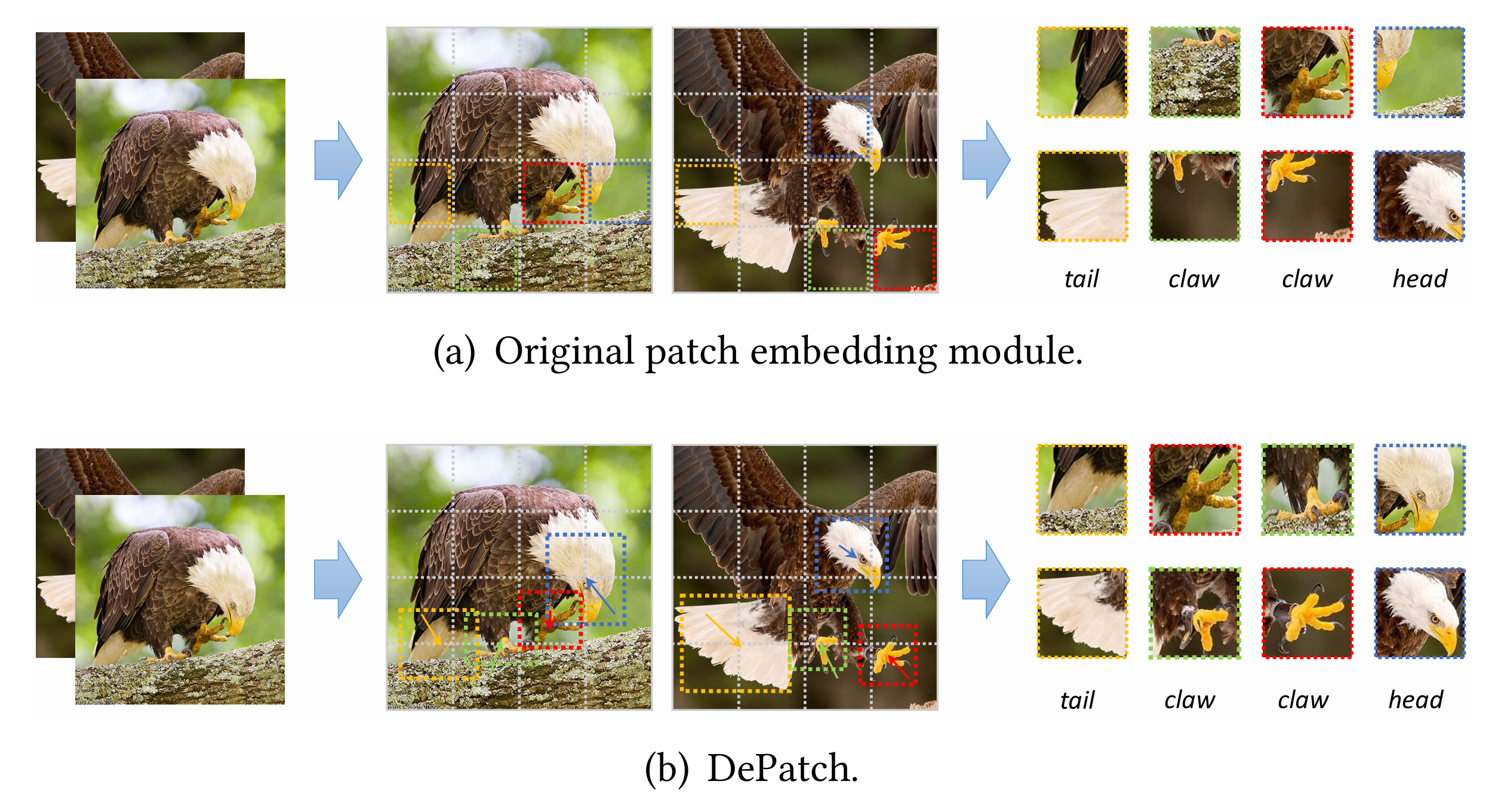
DPT: Deformable patch-based transformer for visual recognition
Zhiyang Chen, Yousong Zhu, Chaoyang Zhao, Guosheng Hu, Wei Zeng, Jinqiao Wang, Ming Tang
ACM Multimedia Conference (ACM MM) 2021 Oral
The fixed-size patch embedding in current vision transformers might overlook local spatial structures and extract inferior image features. To address this problem, we propose a new module (DePatch) which learns to adaptively split the images into patches with different positions and scales in a data-driven way, resulting in an enhanced backbone to extract more potent image features.

All publications
Education
-
 Xi'an Jiaotong UniversityB.S. in AutomationSep. 2015 - Jun. 2019
Xi'an Jiaotong UniversityB.S. in AutomationSep. 2015 - Jun. 2019 -
 Institute of Automation, CASPh.D. at Foundation Model Research CenterSep. 2019 - Jun. 2024
Institute of Automation, CASPh.D. at Foundation Model Research CenterSep. 2019 - Jun. 2024
Experience
-
 SenseTime, BeijingGeneral Vison Model, Self-Supervised Learning
SenseTime, BeijingGeneral Vison Model, Self-Supervised Learning -
 MiHoYo, BeijingLarge Language Models, AI for Game
MiHoYo, BeijingLarge Language Models, AI for Game